Big Bang Theory: The Most Popular Scientific Explanation Of The Beginning Of The Universe

“Big Bang Theory says that about 13.7 billion years ago the universe was created by a massive explosion-like event, from which space, time and matter all started.”
The Big Bang Theory Is The Most Widely Accepted Explanation Of How The Universe Originated. According To This Theory, The Entire Universe Began From An Infinitely Small, Super Hot And Dense Point That Expanded Rapidly From One Point To The Next. This Expansion Process, Which Began About 13.7 Billion Years Ago, Is Still Going On Today — And It Is This Process That Gave Birth To Our Vast, Ever-Expanding Universe.
While Scientists Have Never Seen The Actual Formation Of The Universe Live, We Have Proof Of This Theory From Advanced Mathematical Models, Simulations, And Especially The Cosmic Microwave Background (Cmb). The Cmb Is A Faint “Echo” Of Thermal Radiation That Provides Evidence Of The Early Stage Of The Universe — And Scientists Study It In Detail To Validate The Big Bang Theory.
Although The Big Bang Theory Has Strong Support In The Scientific Community, Some Researchers Also Propose Alternate Theories — Such As Eternal Inflation (In Which The Universe Continuously Expands) Or The Cyclical Universe (In Which The Universe Is Repeatedly Created And Destroyed). The Goal Of These Ideas Is To Explain Unanswered Questions That The Big Bang Theory Does Not Clear Up.
The Beginning Of The Universe
Almost 13.7 Billion Years Ago, The Entire Universe Was Compressed Into An Infinitely Small And Super Hot Singularity — A Point Of Unimaginable Heat And Density.
Then Suddenly A Massive Explosion-Like Expansion Began, In Which The Universe Began To Expand Faster Than The Speed Of Light. This Phase, Called Cosmic Inflation, Lasted For A Duration Of Less Than A Nanosecond (Approx 10^-32 Seconds). This Powerful Theory Was Proposed By Physicist Alan Guth In 1980, Which Changed The Way We Understand The Big Bang.
When This Phase Of Inflation Ended Completely — And In A Way That Is Still Unexplained — The Traditional Big Bang Process Began. This Stage Is Called “Reheating,” In Which There Was A Tremendous Flood Of Matter And Radiation. This Process Gave The Universe Everything That We See Today — Particles, Atoms, Stars And Galaxies — All Of Which Began To Form After This Moment.
What Happened In The First Second Of The Universe? A Journey Immediately After The Big Bang
When The Universe Was Born, A Lot Had Happened In Just The First Second. According To Nasa, The Temperature Of The Universe At That Time Was About 10 Billion Degrees Fahrenheit (Ie 5.5 Billion Celsius) – Nothing Was Normal, So Much So. During This Extreme Heat, Fundamental Particles Like Neutrons, Protons And Electrons Were Formed. These Particles Were Going To Become The Building Blocks Of Stars, Planets, And Galaxies.
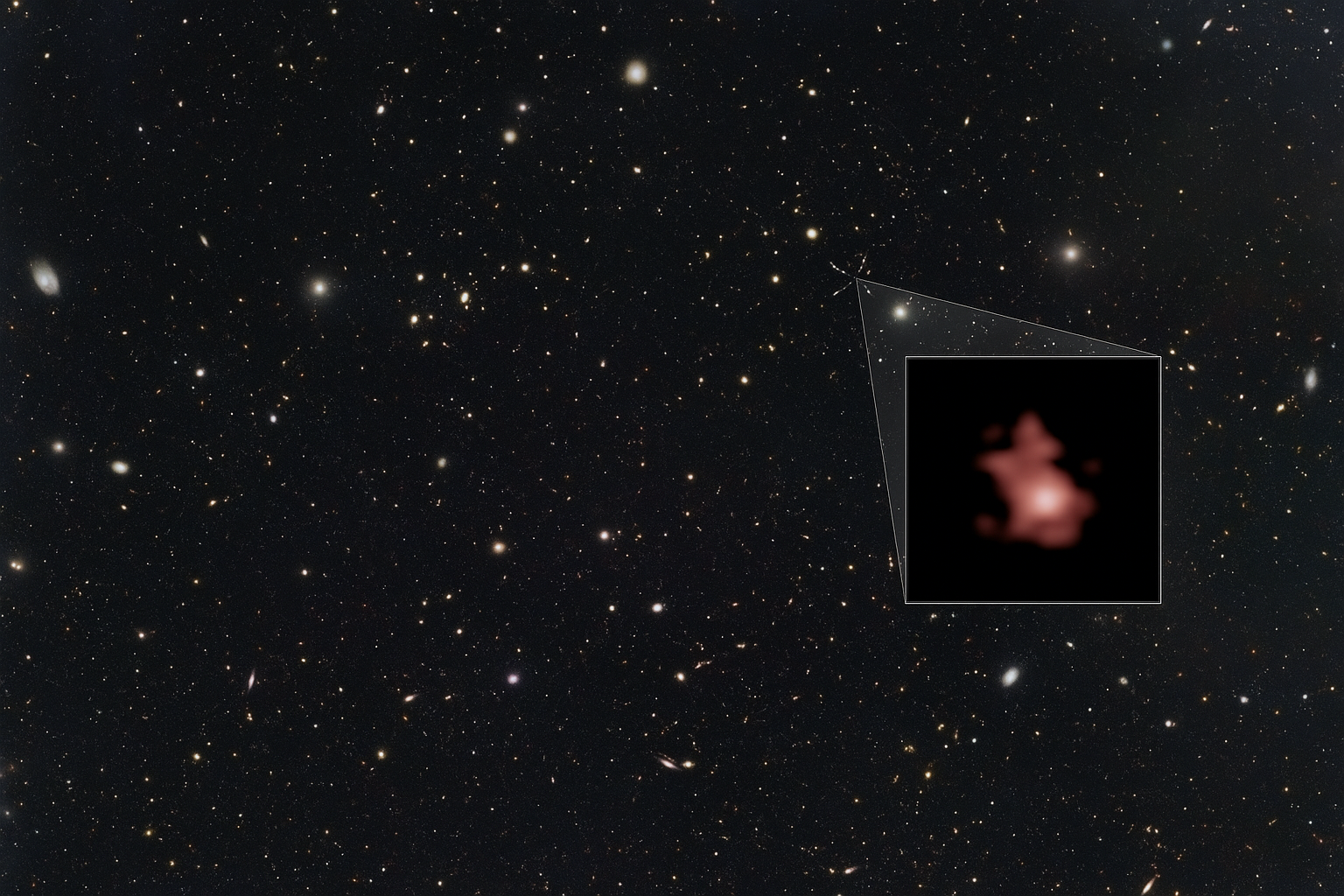

“The Hubble Space Telescope has captured an image of the galaxy Ganymede-11 that shows how this small galaxy looked shortly after the Big Bang.”
The Universe At That Time Was Like A Super Hot Particle Soup, Where Visible Light Could Not Stick. According To Nasa, The Free Electrons Present In The Universe Were Constantly Scattering Photons (Light Particles) – Just Like Sunlight Scatters After Colliding With Water Droplets In Clouds.
But With Time, These Free Electrons Started To Combine With The Nuclei To Form Neutral Atoms – In Which The Positive And Negative Charges Got Balanced.
Only After This Process Was Complete, The Light Started To Travel Freely – And This Moment Came About 380,000 Years After The Big Bang.
We Today Know This Light As The “Afterglow Of The Big Bang”. Its Proper Scientific Name Is The Cosmic Microwave Background (Cmb). It Was First Predicted By Ralph Alpher And Some Other Scientists In 1948. But The Interesting Thing Is That This Discovery Happened Accidentally, Almost 20 Years Later, When Scientists Actually Detected This Light Signal.
Accidental Discovery Of Cosmic Microwave Background – A Scientific Twist
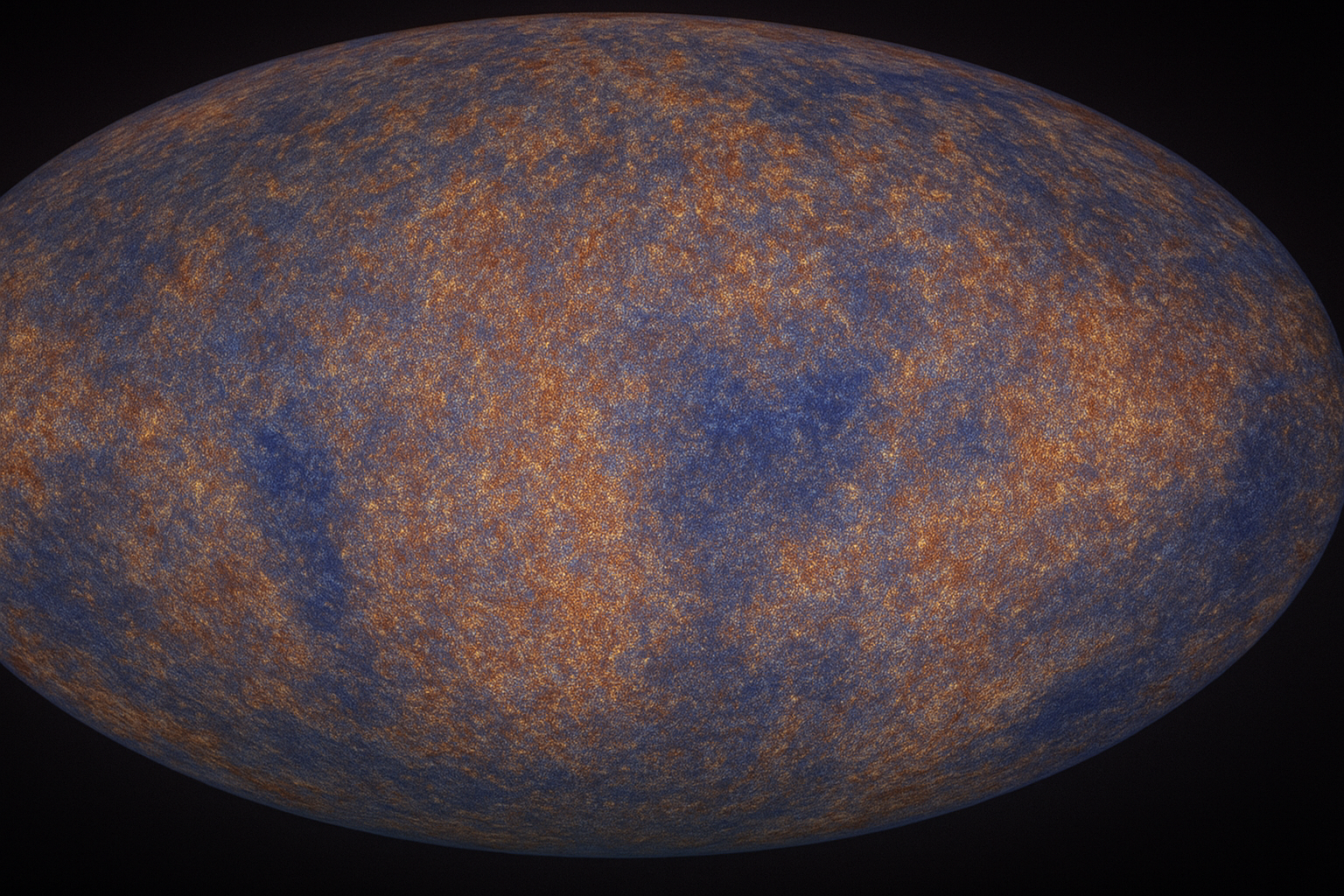
“ESA’s Planck spacecraft created a detailed map of the background radiation left after the Big Bang, in which the oldest light of the universe has been captured. This valuable data helps scientists to know the exact age of the universe.”
In 1965, An Accidental Discovery Took A Historic Step Towards Proving The Big Bang Theory. Arno Penzias And Robert Wilson, Working At Bell Telephone Laboratories (New Jersey), Were Developing A Radio Receiver. According To A Nasa Article, They Captured Much Higher Temperature Signals From The Receiver Than Expected, Which Was Beyond Understanding.
At First, They Thought The Disturbance Might Be Caused By The Pigeons Nesting Inside The Antenna And Their Waste. They Cleaned The Antenna, Removed The Pigeons – Even Killed Them – But Still Kept Getting That Strange Radio Signal.
During This Time, A Team At Princeton University, Led By Robert Dicke, Was Busy Looking For Evidence Of Signals From The Cosmic Microwave Background (Cmb). When They Heard About The Unusual Observations Of Penzias And Wilson, They Immediately Realized That This Was The Cmb Signal They Had Been Trying To Trace For So Long.
Finally, Both Teams Published Their Research Papers In The Astrophysical Journal In 1965. This Discovery Was Not Only A Major Scientific Breakthrough, But It Also Provided Solid Observational Proof In Support Of The Big Bang Theory – And Made History.
Big Bang Theory FAQs Answered By An Expert
Has Big Bang Theory Been Proven?
If You Are Wondering Whether Big Bang Theory Is 100% Proven, Then The Simple Answer Is — Saying “Scientifically Completely Proven” Would Not Be Correct. In Science, Theories Cannot Be Proved Mathematically Like Equations Are Proved In Maths. But, There Is Very Strong Scientific Evidence In Support Of Big Bang Theory. Every Scientific Test And Observation Has Gone In Favour Of This Theory.
So In Short, Whatever Observational Data We Have Got, Matches With The Predictions Of Big Bang Theory. Here Are The 3 Most Important Evidences That Support This Theory:
- Hubble’s Law – The Universe Is Expanding
Hubble Observed That The Farther The Galaxies Are, The Faster They Are Moving Away From Us. This Means That The Universe Is Expanding In All Directions. It Also Shows That There Was A Time When Everything Was Concentrated In A Single Point.
- Cosmic Microwave Background (Cmb)
Cmb Is An Ancient Light That Remained After The Big Bang. Its Properties Tell That The Universe Was Once In A Plasma (Ionized Gas) Stage, Which Later On Converted Into Neutral Gas. This Transition Happened Approximately 380,000–400,000 Years After The Big Bang, And It Confirms That The Initial Universe Was Extremely Hot And Dense.
- Quantity Of Light Elements – Big Bang Nucleosynthesis (Bbn)
Elements Like Helium-4, Helium-3, Lithium-7 And Deuterium Were Created Immediately After The Big Bang, In Just A Few Minutes. This Process Is Called Big Bang Nucleosynthesis (Bbn). The Quantity Of These Observed Today Confirms That The Universe Was Extremely Hot And Dense In The Beginning – Approximately 10 Lakh Times Hotter Than The Cmb Phase!
Does Anything Contradict The Big Bang Theory?
Till Now No Such Solid Observation Has Been Found That Rejects The Big Bang Theory. Yes, Some Questions Have Definitely Been Raised In The Simple Big Bang Model, Such As:
Why Is The Cmb Temperature The Same In Every Direction?
Why Does The Universe Appear Flat?
Why Do The Size And Shape Of Galaxy Clusters Not Match The Predicted Ones?
The Solution To These Problems Was Found In The Inflation Theory – Which Is An Extended Part Of The Big Bang Theory. According To This, There Came A Moment When The Universe Expanded Super-Fast From Zero, Which Explains These Issues.
When Did The Big Bang Theory Come? Who Created It?
Edwin Hubble First Observed In The 1920s That Galaxies Were Moving Away From Us – And This Discovery Formed The Basis Of The Big Bang Theory.
Then In The 1970s The Cosmic Microwave Background (Cmb) Was Discovered, Which Gave Further Confirmation To The Theory.
The Term “Big Bang” Was First Used By Astronomer Fred Hoyle In The Late 1940s – He Used It Ironically To Mock The Term, But Later It Became The Most Popular Name!
Modelling The Big Bang
We Cannot Observe The Big Bang Directly – Because This Event Happened Almost 13.8 Billion Years Ago. But This Does Not Mean That Scientists Have Given Up Hope. With The Help Of Today’s Modern Tools And Supercomputers, Researchers Are Finding New Ways To Understand The Birth Moment Of The Universe.
Reverse Engineering Of The Big Bang With Supercomputer Simulations
In 2021, Cosmologist Masato Shirasaki Of Japan’s National Astronomical Observatory And His Team Conducted A Fascinating Experiment. They Ran A Simulation Of 4,000 Virtual Universes On A Massive Supercomputer — With The Goal Of Simulating Some Of The First Moments After The Big Bang.
Masato Shirasaki Told Live Science:
“We Are Doing Something Like Imagining Someone’s Baby Photo By Looking At Its Latest Image.”
The Researchers Simulated Those Virtual Universes Backward Using Current Data About The Universe (Such As The Position, Motion And Gravity Effects Of Galaxies). Their Goal Was To Understand That If The Starting Point Of Their Simulations Turned Out To Be Accurate, They Could Guess What Our Real Universe Would Have Looked Like At The Time Of The Big Bang.
Antimatter Vs Matter: Another Perspective To Understand The Origin Of The Universe
Some Scientists Have Approached This Topic From Another Angle. In A 2020 Study, Researchers Explored The Imbalance Between Matter And Antimatter – Which They Linked To Dark Matter.
According To This Research, Something Must Have Happened In The Very First Moments After The Big Bang Due To Which Matter Became More Than Antimatter. Due To This Imbalance, Dark Matter Must Have Also Formed – Which Still Affects Gravity In The Universe, But Does Not Interact With Light.
The Age Of The Universe
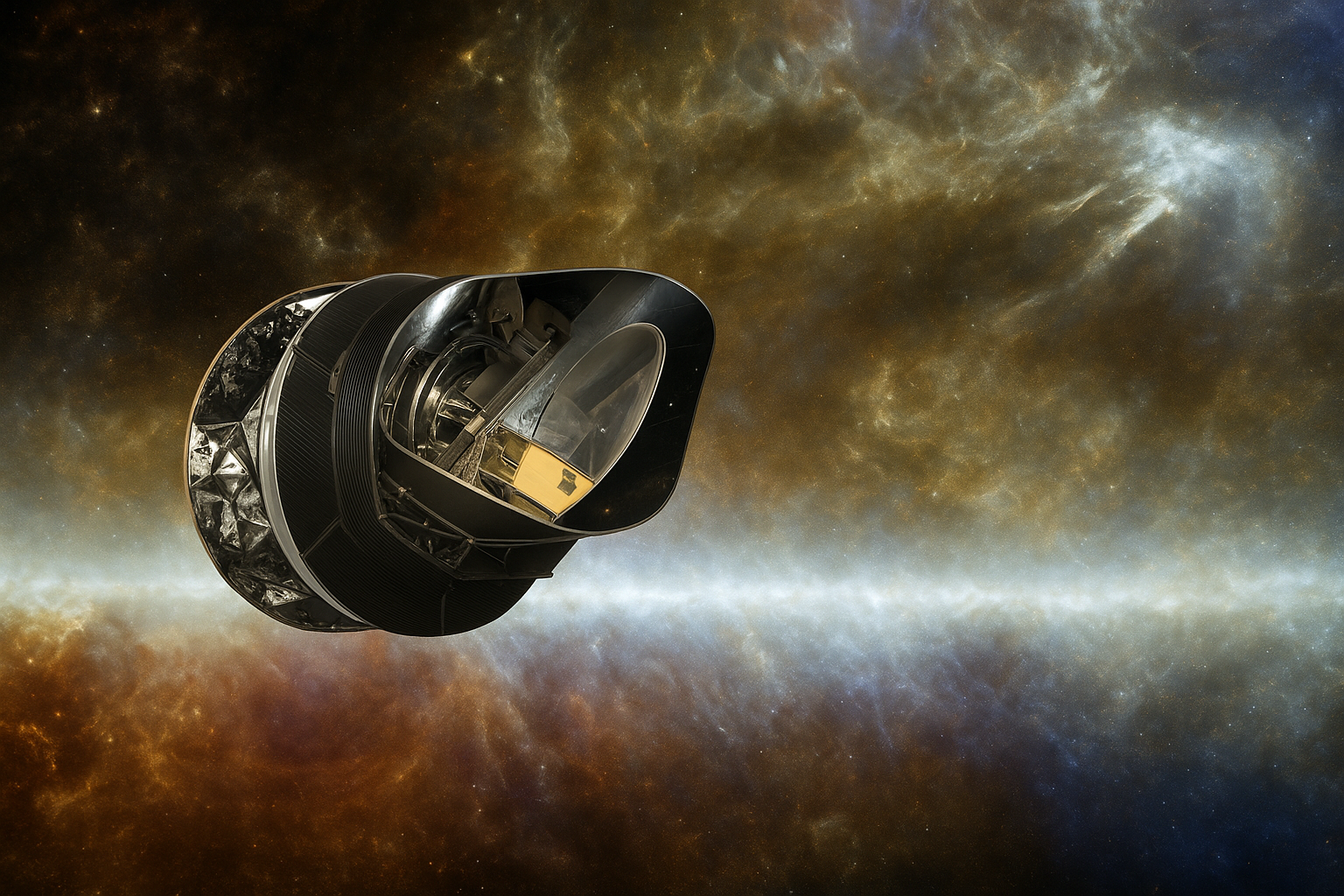

“This image is an artist’s impression of the European Space Agency’s Planck spacecraft. Planck’s main mission was to study the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) — the oldest radiation left after the Big Bang.”
What Is Cmb? Know About Cosmic Microwave Background
Cmb (Cosmic Microwave Background) Is A Radiation That Keeps The Memories Of The Ancient Universe Alive. This Mysterious Signal Has Been Observed By Many Top Scientists And Researchers In The World Through Different Space Missions.
The First And Most Famous Mission Was Nasa’s Cobe Satellite (Cosmic Background Explorer), Which Was Launched In The 1990s. This Satellite Made A Detailed Map Of The Entire Sky, Which Helped Scientists Understand The Origin Of The Universe.
Many Important Missions Came After Cobe, Such As:
Boomerang Experiment (Balloon Observations Of Millimetric Extragalactic Radiation And Geophysics)
Nasa’s Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (Wmap)
Esa’s Planck Satellite (European Space Agency)
Among These, The Planck Satellite Collected The Most High-Resolution Data Of The Cmb. This Satellite Shut Down On 23 October 2013, But The Data Collected By It Is Still A Treasure For Scientists, In Which New Discoveries Are Being Made.
Some Unique Questions Related To Cmb
The Maps Of Cmb Have Also Shown Some Surprising Things. For Example, The Southern Hemisphere Appears Slightly Redder (I.E. Warmer) While The Northern Hemisphere Is Comparatively Cooler. This Observation Goes Against The Big Bang Theory, Because According To The Theory The Cmb Should Be Equal In Every Direction.
Truth Of The Universe: Only 5% Is Visible
A Detailed Analysis Of The Cmb Helps Astronomers Understand What The Universe Is Made Of. According To Research:
Only 5% Of The Universe Is Made Of The Matter We Can See — Like Stars, Planets, And Galaxies.
The Remaining 95% Of The Universe Is Invisible — What We Know As Dark Matter And Dark Energy, Which Cannot Yet Be Directly Measured With Scientific Tools.
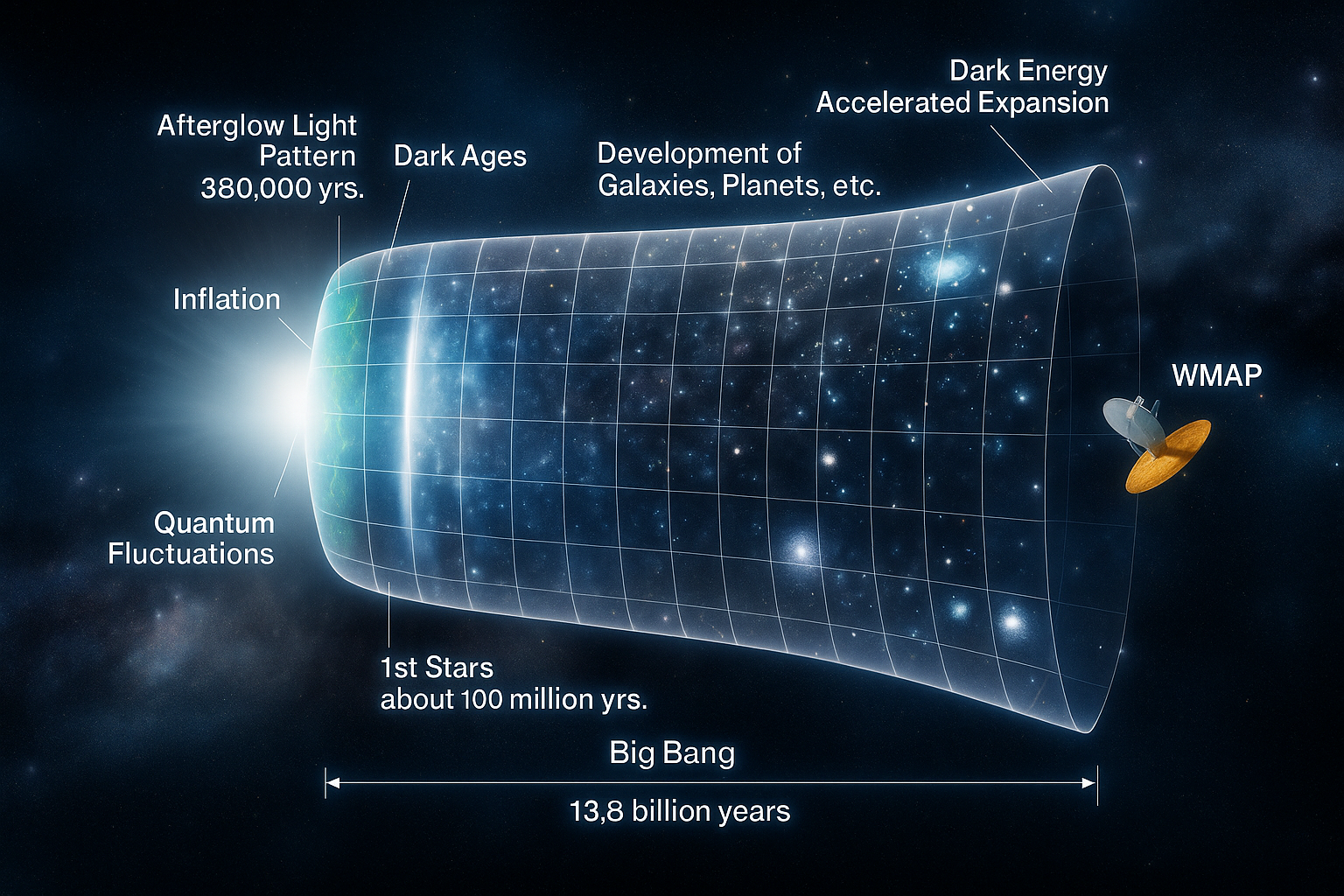
“This graphic shows the complete timeline of the universe based on the Big Bang theory and inflation models — explaining how the universe developed from the beginning till today.”
Was The Big Bang An Explosion
Was Big Bang Really An Explosion? Understand From The Point Of View Of Science
When We Think About Big Bang Theory, A Scene Of A Huge Explosion Often Comes To Our Mind. But The Truth Is That Big Bang Was Not A Typical Explosion. This Image Is A Bit Misleading.
What Happens In A Normal Explosion? All Fragments Fly From A Central Point Inside And Outside The Existing Space. If You Are At That Central Point, You Will See That All Fragments Are Moving Away From You At The Same Speed.
So Was There A Big Bang?
The Big Bang Was Not A Blast, But Rather The Expansion Of Space Itself – The Concept Of Which Comes From Einstein’s General Relativity Equations. This Idea Is Very Different From Classical Physics (Which We Use In Daily Life). In It, Both Space And Time Are Changing, Not Just Objects Are Moving.
How Is The Universe Expanding?
This Simply Means That Distances In Every Corner Of The Universe Are Increasing – Everything Is Being Stretched.
If The Distance Between Two Galaxies Is X, Then They Are Moving Away From Each Other At A Specific Speed.
And If A Galaxy Is 2x The Distance, It Will Be Moving Away At Double The Speed.
This Expansion Is Uniform, Meaning Space Expands At The Same Rate Everywhere — There Is No Central Point From Which Everything Is Spreading.
The Rate Expansion Of The Universe
Hubble Constant And Hubble Tension: Mystery Of Universe's Expansion
The Speed At Which The Universe Is Expanding Is Called Hubble Constant. This Is A Key Concept That Helps Us Understand How The Universe Changes With Time, And What Shape It Will Have In The Future.
But Behind This Simple-Looking Concept Is Hidden A Big Scientific Mystery – Which We Know As “Hubble Tension”.
Hubble Constant: Each Method Gives Different Results
When Scientists Measure The Expansion Rate Of The Universe, They Get Different Values of The Hubble Constant — Depending On The Method Used To Measure It:
Some Researchers Derive The Value By Studying The Afterglow Of The Big Bang (Such As Cmb – Cosmic Microwave Background).
On The Other Hand, Some People Calculate The Hubble Constant By Measuring The Distances And Motions Of Galaxies.
What Is Hubble Tension?
The Problem Is That The Results Of These Two Methods Do Not Match. This Difference Is What Scientists Have Named Hubble Tension.
This Mismatch Is So Confusing That Even Scientists Are Surprised. Till Date No One Knows Exactly Why This Gap Exists. Is There Some Error? Or Are We Still Missing Some Important Things About The Universe?
Is This A Signal Of New Physics?
Many Experts Believe That This Hubble Tension Is Perhaps Leading Us Towards Some New Physics – Theories That Go Beyond Einstein’s Relativity And Give Us A Chance To Understand The Universe From A New Angle.
JWST And The Big Bang

“The James Webb Space Telescope is so powerful that it has the ability to look into the deepest past of the universe – where no telescope has been able to reach till now.”
James Webb Telescope: A Glimpse That Can Go To The Beginning Of The Universe
Do You Know That A Telescope Is A Kind Of Time Machine? It Gives Us A Chance To Look Into The Past Of The Universe, I.E. The Past.
Nasa’s Hubble Space Telescope Showed Us How Galaxies Looked Thousands Of Crores Of Years Ago – And It Started A New Era Of Space Exploration.
James Webb: Advanced Version Of Hubble
Now Hubble’s Successor, I.E. James Webb Space Telescope (Jwst), Can Look Even Deeper Into The Universe. Nasa Hopes That Jwst Will Show Us A Glimpse Of 13.6 Billion Years Old Galaxies – When The First Galaxies Were Formed.
Jwst Sees In The Infrared — And That Is Its Greatest Power.
The Hubble Telescope Mostly Observes In Visible Light, Which Is What Human Eyes Can See.
But Jwst Is An Infrared Telescope, Which Means It Can Also Detect Heat Signals And Stretched Light Waves — Which Come From Very Distant Galaxies.
As The Universe Expands, The Light Waves Coming From Distant Galaxies Get Stretched. The Light That Was Visible Before Has Now Become Infrared. And That Is Why The James Webb Telescope Is Much More Powerful Than Hubble In Seeing Them.
