The Future Of The Universe
What Determines The Fate Of The Universe?
The Future Of The Universe Hinges On The Delicate Balance Between Two Fundamental Cosmic Forces:The Momentum Of Expansion – Which Is Causing The Universe To Accelerate OutwardThe Force Of Gravity – Which Attempts To Draw The Universe Back Inward These Opposing Forces Will Ultimately Dictate Whether The Universe Will Expand Indefinitely, Reach A Standstill, Or Eventually Collapse Under Its Own Gravity.
1. How Accurately Can We Predict The Future Of The Universe?
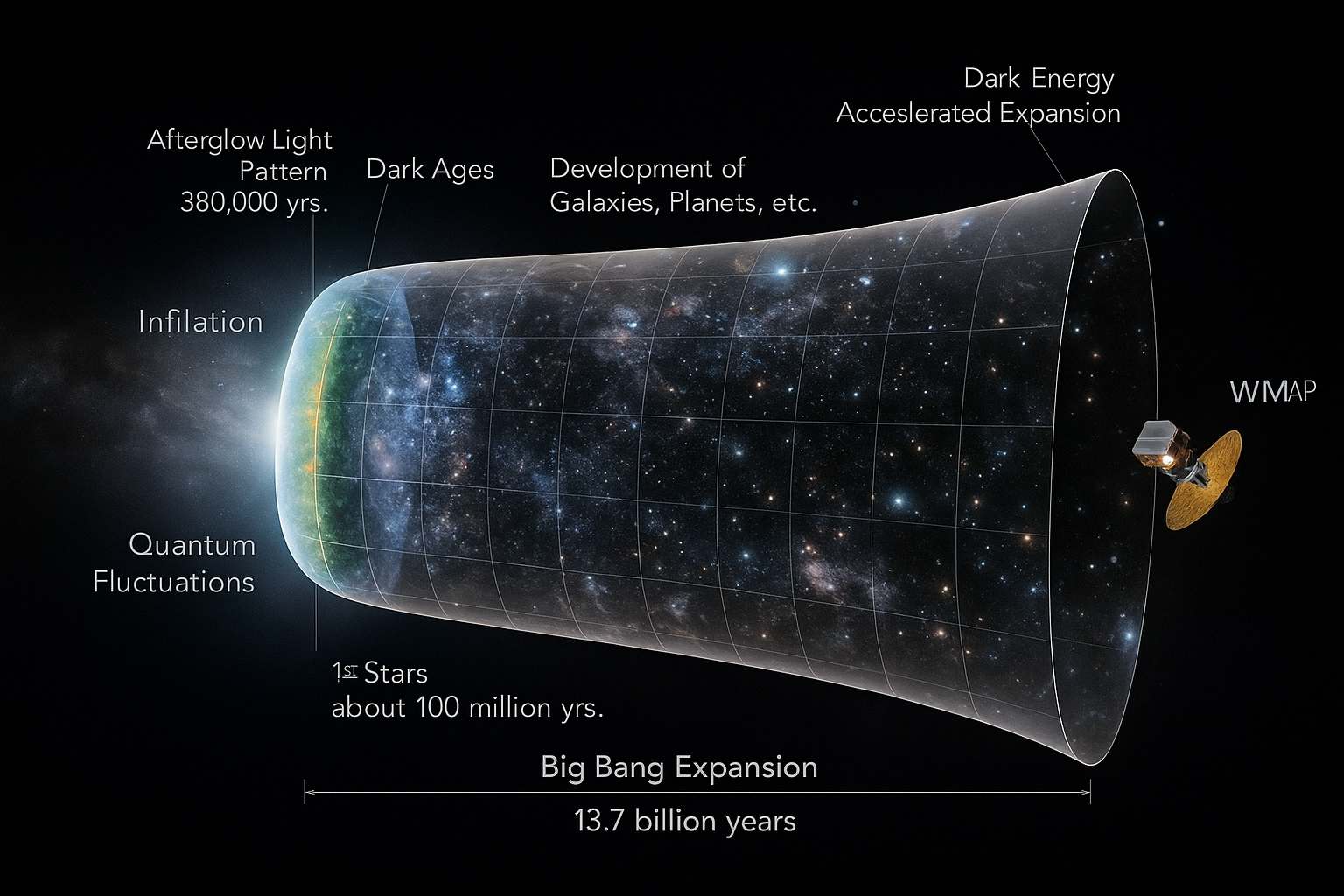
Credit-NASA/WMAP Science Team
Our Ability To Predict The Universe’s Future Depends Entirely On How Much Of It We Can Actually Observe.
About The Image
The Image Shows The Evolution Of The Universe Over The Last 13.7 Billion Years. On The Left Side, We See The Big Bang, Which Marked The Birth Of The Universe.This Was Followed By A Phase Of Rapid, Exponential Expansion, Known As Cosmic Inflation.
The Vertical Scale Represents The Growing Size Of The Universe Over Time.
From Slowing Down To Speeding Up: How The Universe Expands
For The First Few Billion Years, The Expansion Of The Universe Gradually Slowed Down — Due To The Pull Of Gravity On Matter.
However, In More Recent Times, The Universe’s Expansion Has Started To Accelerate Again.
the Driving Force Behind This Renewed Acceleration?
Dark Energy — A Mysterious, Repulsive Force That Pushes Space Apart And Fuels The Ongoing Expansion Of The Cosmos.
The Cosmological Principle
The Theoretical Foundation For Scientists’ Projections About The Universe’s Destiny Lies In:
“The Cosmological Principle” –
This Principle Asserts That The Laws Of Physics Are Uniform And Universal, Applying Equally Across Every Region Of The Cosmos — Whether It’s Earth Or A Remote Galaxy.This Principle Enables Us To Construct A Precise Cosmological Model — And To Gain Profound Insights Into The Possible Evolutionary Path Of The Universe.
How Is The Future Of The Universe Predicted?
To Forecast The Universe’s Destiny, Scientists Rely On A Fundamental Principle: The Influence Of Gravity On Matter Shapes The Universe
And This Geometrical Structure Determines Its Future.
What Is Critical Density?
Critical Density Refers To: The Exact Average Density Of Matter In The Universe Required For Gravity To Eventually Halt Its Expansion —
But Only After An Infinite Amount Of Time. This Concept Leads To Three Possible Cosmic Outcomes, Based On How The Actual Density Compares To The Critical Density:
That Shape The Universe’s Fate:
If Density > Critical Density
The Universe Will Ultimately Contract And End In A Big Crunch
If Density = Critical Density
The Universe Will Continue To Expand Forever, But At A Gradually Slowing Rate – Known As The Big Freeze
If Density < Critical Density
The Universe Will Expand At An Ever-Accelerating Pace, Leading To A Big Rip
Scenario 1: Closed Universe – Can The Cosmos Collapse?
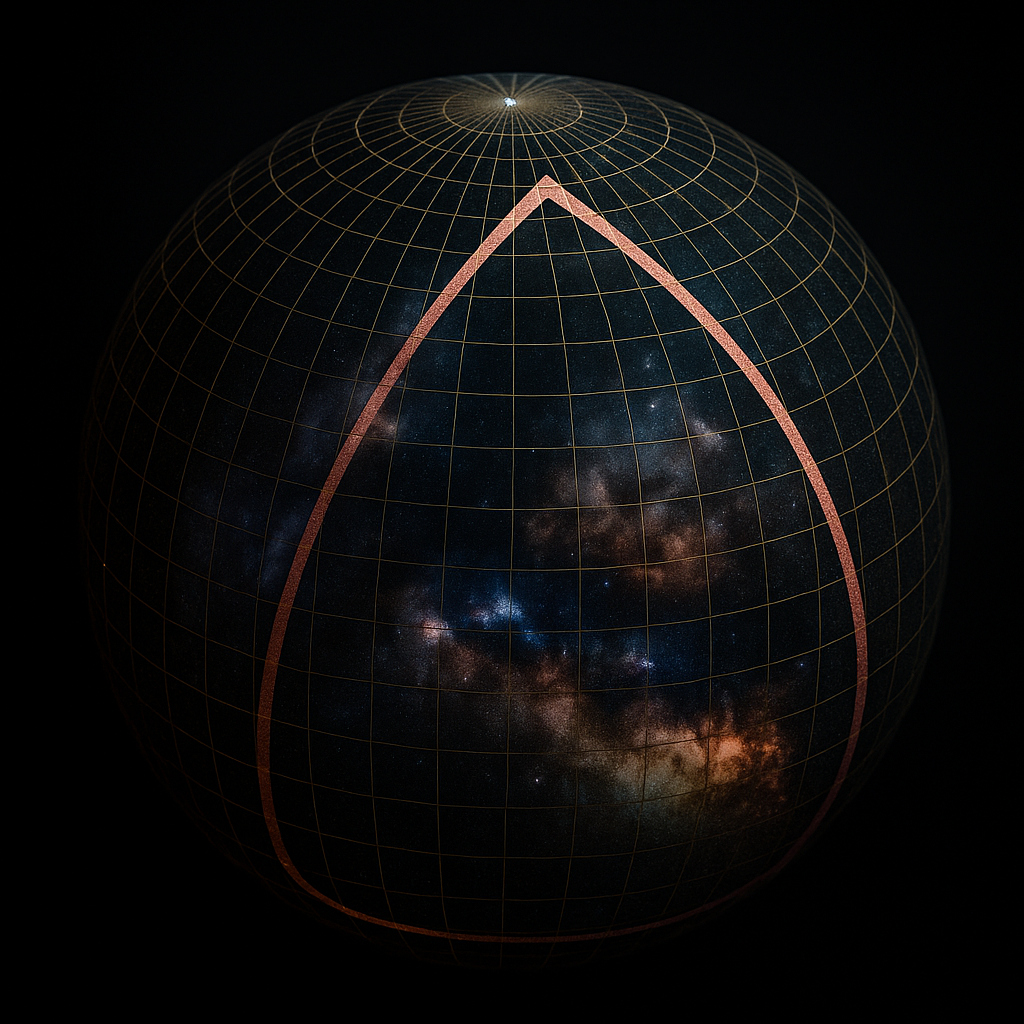
If The Density Of The Universe Exceeds The Critical Threshold,
Then Gravitational Forces Become So Dominant That They Gradually Decelerate The Universe’s Expansion,
Bring It To A Halt, And Eventually Cause It To Contract Inward — Essentially Reversing The Direction Of Cosmic Motion.
Shape Of Space-Time: Spherical Geometry
In This Scenario, The Structure Of Space-Time Is Curved Like A Sphere.
If You Draw A Triangle On This Non-Euclidean Surface,
Its Interior Angles Will Sum To More Than 180° —
A Key Indicator Of Positive Curvature In Space.
Endgame Name: The Big Crunch
In A Closed Universe, Gravity Eventually Overpowers Expansion,
Drawing Galaxies, Stars, And All Forms Of Matter Into A Single, Collapsing Point —
An Event Known As The Big Crunch. This Catastrophic Collapse Is Often Seen As The Mirror Image Of The Big Bang. Some Theories Even Propose That A New Universe Might Emerge From This Singularity
In A Kind Of Cosmic Rebirth Through Another Big Bang.
Scenario 2: Open Universe – Will The Cosmos Expand Forever?
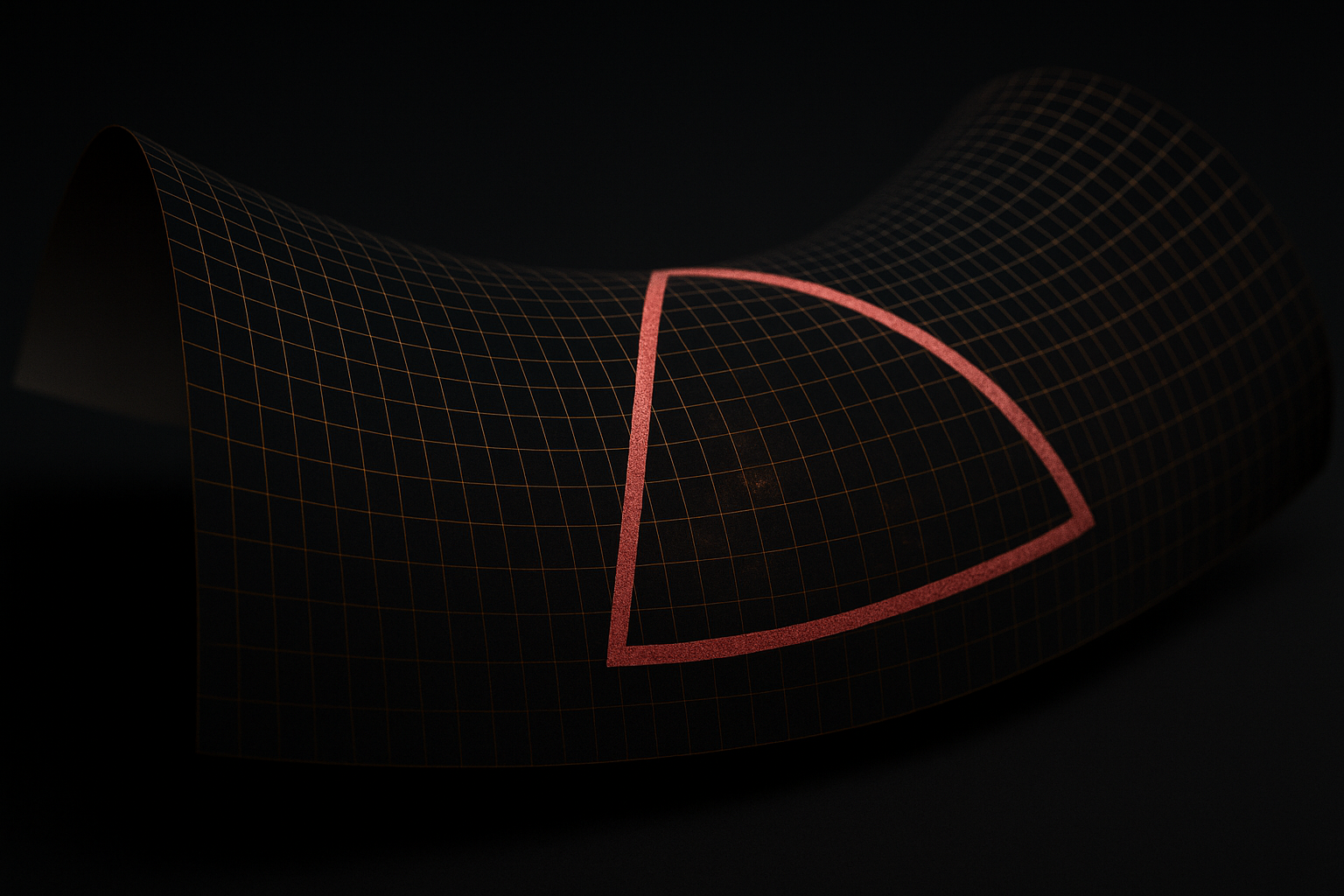
If The Matter Density Of The Universe Is Lower Than The Critical Value,
Then Gravity Is Too Feeble To Counteract The Expansion.
As A Result, The Universe Will Continue To Expand Indefinitely,
Though The Rate Of Expansion Will Gradually Decelerate Over Time.
Cosmic Geometry: Saddle-Shaped Curvature
In This Scenario, The Fabric Of Space-Time Takes On A Hyperbolic Or Saddle-Like Geometry.
If You Draw A Triangle On This Negatively Curved Surface,
The Sum Of Its Interior Angles Will Be Less Than 180° —
A Key Indication That Space Is Curved Outward, Not Flat.
Ultimate Fate: The Big Chill
As The Universe Expands Endlessly, A Point Will Arrive When All Stars And Galaxies Burn Out And Exhaust Their Nuclear Fuel. At That Stage, The Cosmos Will Become Increasingly Cold, Dark, And Barren. Scientists Refer To This Fate As The Big Chill Or Heat Death. A State Where No Light, No Warmth, And No Life Remain. Everything Will Descend Into Eternal Silence And Stillness, Marking The Universe’s Thermodynamic Demise.
Scenario 3: Flat Universe – No Collapse, No Rapid Expansion, Just Gradual Cooling
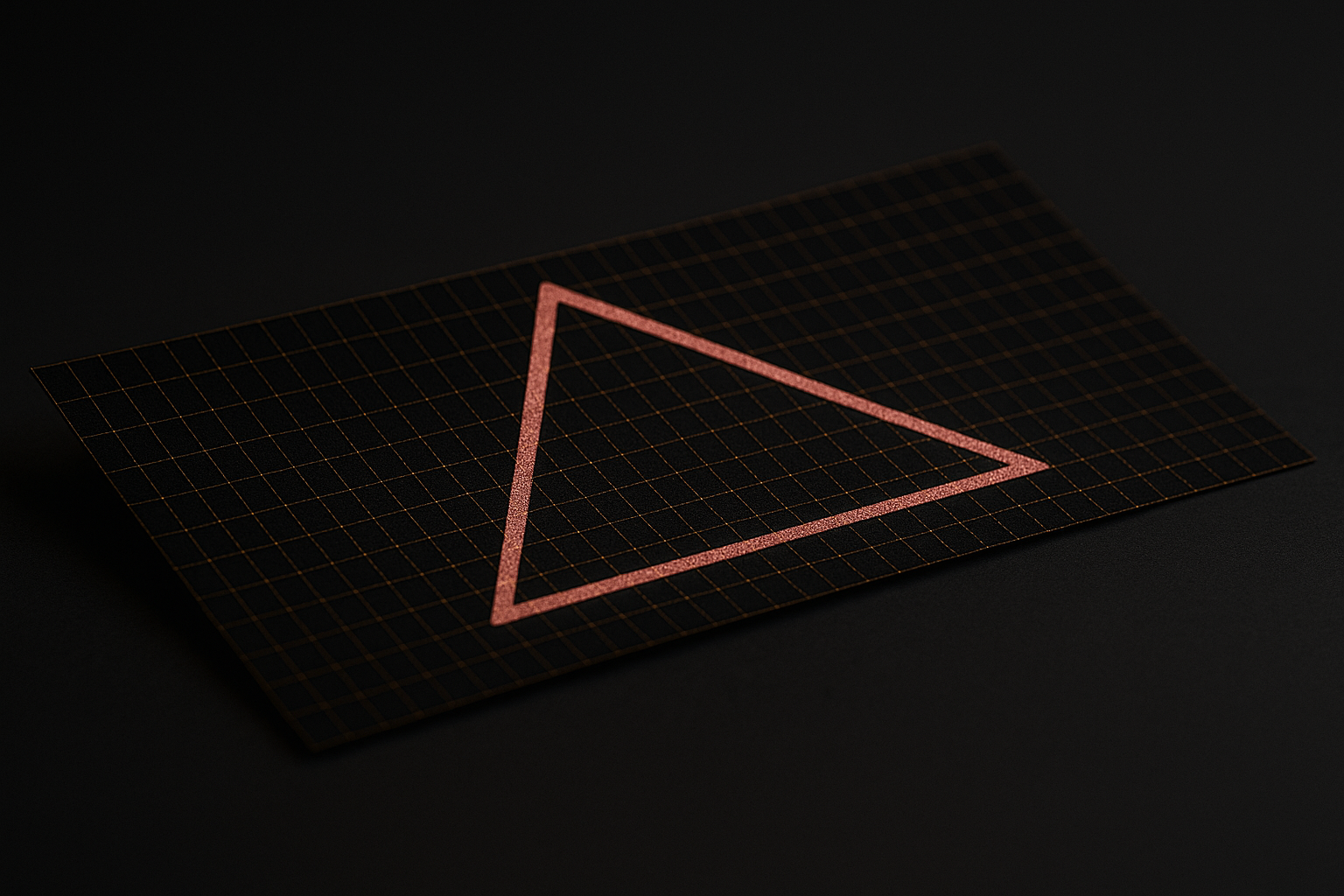
If The Universe’s Density Is Precisely Equal To The Critical Density,
Then Gravity Is Strong Enough To Gradually Counterbalance Expansion
But Only After An Infinite Duration. In Practical Terms, The Universe Never Fully Halts; It Just Expands More And More Slowly.
Structure Of Space-Time: Perfectly Flat Like A Plane
The Geometry Of A Flat Universe Is Euclidean
Uniformly Straight And Level, Like An Endless Sheet Of Paper. In This Configuration, If You Draw A Triangle, The Sum Of Its Internal Angles Is Always Exactly 180° A Hallmark Of Zero Curvature In Space.
Cosmic Destiny: The Gradual Big Freeze
In A Flat Universe, Expansion Continues Indefinitely
But The Rate Of Expansion Slows Down Progressively —
Slower Than In An Open Universe.As The Cosmos Stretches, Energy And Thermal Radiation Become More Uniformly Dispersed.Eventually, The Universe Reaches A State That Is:
Cold, Inert, And Devoid Of Life
A Fate Known As The Big Freeze.This Final Stage Marks A Future Where:
Every Region Of The Universe Becomes Thermally Balanced And Frigid,
And No New Energy Exchange Or Activity Can Take Place.
What’s The Most Probable Fate Of Our Universe?
If We Truly Wish to Understand the Future of the Universe…The first step is to determine the average density of the Universe —
a critical factor that influences its ultimate fate.
What Did Astronomers Believe 30 Years Ago?
Around three decades ago, scientists assumed that the Universe was composed solely of visible matter such as stars, galaxies, and biological life like ourselves.These components are classified as ‘ordinary’ or baryonic matter material that is visible, tangible, and possesses mass.
What Do Modern Scientists Emphasize?
Contemporary astronomical research and deep-sky observations have revealed that the Universe contains numerous invisible elements which, although undetectable to the naked eye, exert a significant influence on the Universe’s expansion.
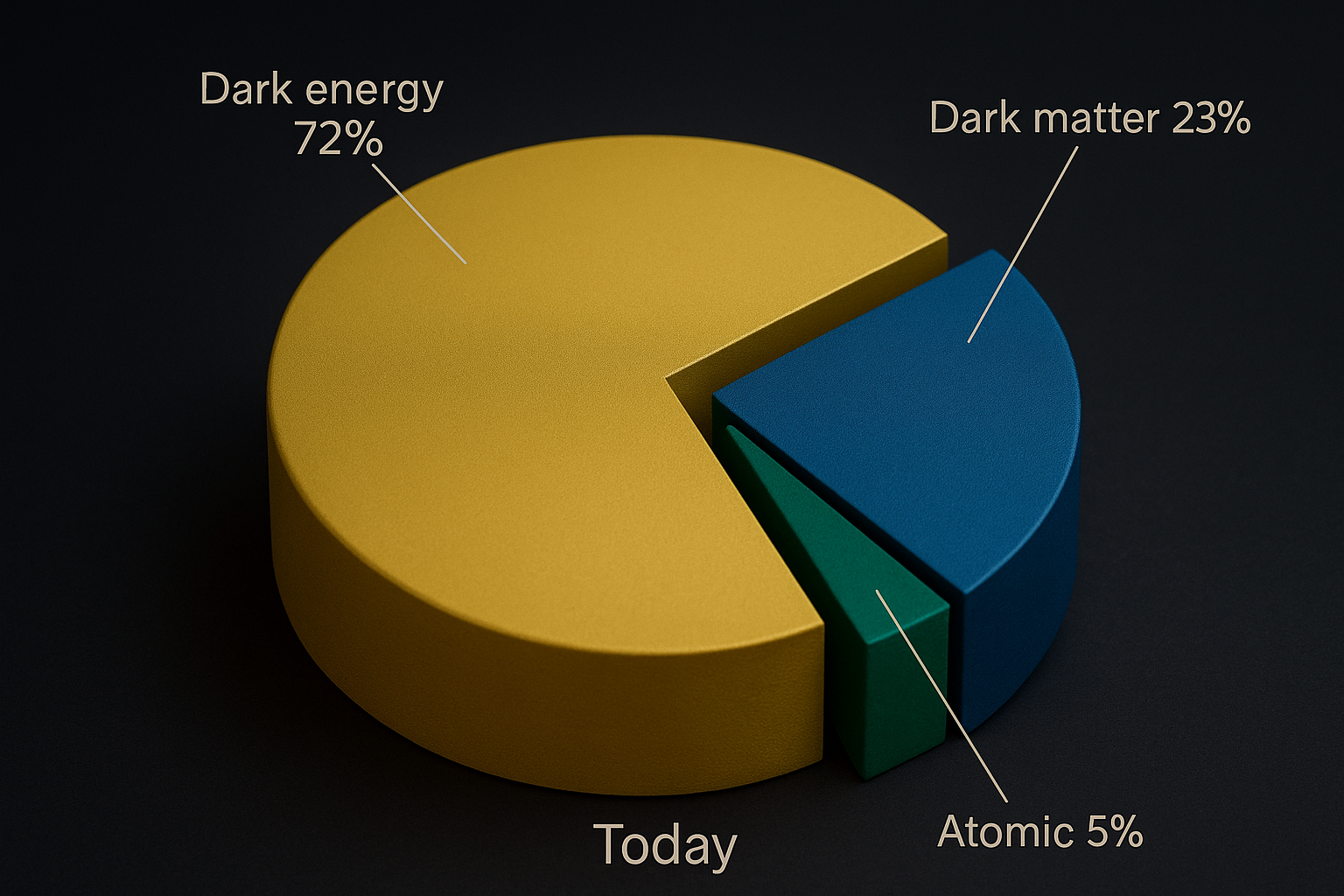
According to Modern Cosmology – What Is the Universe Made Of?
Today’s cosmologists identify four primary constituents of the Universe:
1. Radiation Light particles and energy waves
that are uniformly distributed throughout space
2. Baryonic Matter – Planets, stars, galaxies, and living organisms
composed of atoms and subatomic particles
3. Dark Matter – An invisible substance that doesn’t emit light
but reveals its presence through gravitational interactions
4. Dark Energy – A mysterious, repulsive force
responsible for the accelerating expansion of the Universe
What Is Radiation? – Explained In Simple Words
Radiation Refers To High-Speed Particles Or Waves That Either Have No Mass (Like Photons)
Or Extremely Tiny Mass (Like Neutrinos).These Particles Move At The Speed Of Light And Carry Energy As They Travel Through Space.
Two Common Types Of Radiation:
Photons – These Are Light Particles That Transmit Both Light And Thermal Energy.
They Are Massless And Form The Basis Of Electromagnetic Radiation.
Neutrinos – These Are Ultra-Light Subatomic Particles,
Produced During Nuclear Reactions Like Fusion In Stars (E.G. The Sun).
Though They’re Almost Invisible And Hardly Interact, They Pass Through Matter All The Time.
These Energetic Particles Are Present Throughout The Cosmos
In Stars, Galaxies, And Even In Everyday Radiation Sources Around You.
What Is Baryonic Matter? – Simple Yet Smart Explanation
Baryonic Matter, Also Known As Ordinary Matter, Refers To Everything We Can See, Touch, Or Physically Interact With — Including Us!
What Fundamental Particles Make Up This Matter?
Baryonic Matter Is Composed Of Three Key Subatomic Particles:
1. Protons
2. Neutrons
3. Electrons
These Particles Combine To Form Atoms,
Which Are The Building Blocks Of All Physical Structures.
What Do Atoms Form?
When Atoms Come Together, They Form:
1. Planets
2. Stars
3. Humans
4. Galaxies
Basically, The Entire Visible Universe That We Can Observe And Experience.
Did You Know?
Baryonic Matter Makes Up Only 5% Of The Total Universe!
The Remaining 95% Is Made Of Dark Matter And Dark Energy,
Which We Can’t See — But They Shape The Universe In Powerful Ways.
What Is Dark Matter? – Understand In Clear Words
You Might Have Heard That Not Everything In The Universe Is Visible To The Human Eye —
And This Cosmic Enigma Is Addressed By The Concept Of Dark Matter.
The Problem: A Gravitational Mystery
Astrophysicists Have Made Some Puzzling Observations:
Galaxy Clusters Remain Gravitationally Bound,
Even Though The Amount Of Visible Matter Seems Insufficient To Hold Them Together.
Spiral Galaxies Spin At Extremely High Velocities,
Yet They Do Not Tear Apart — As If Some Invisible Force Is Maintaining Their Structure.
Scientific Interpretation: Dark Matter
To Explain This, Scientists Proposed The Existence Of An Unseen Substance Known As Dark Matter.
This Form Of Matter Does Not Emit, Absorb, Or Reflect Light,
Which Is Why It’s Referred To As “Dark.”
However, Its Gravitational Pull Can Be Clearly Observed,
Especially In The Rotation And Formation Of Galaxies.
What Do Scientists Currently Know About Dark Matter?
Dark Matter Has Not Been Directly Detected So Far
It Does Not Interact With Electromagnetic Radiation
Meaning It Doesn’t Respond To Light, Heat, Or Radio Waves
Its Presence Is Inferred Through Gravitational Effects
The Mystery Remains Unsolved
Scientists Are Still Debating Fundamental Questions Like:
What Is The True Nature Of Dark Matter?
Is It Made Of Undiscovered Particles?
Or Is It A Sign Of New Physics We Don’t Yet Understand?
So, Is Dark Matter Real?
Even Though We Have Never Directly Observed It,
The Theory Of Dark Matter Remains One Of The Most Powerful Explanations
For The Behavior Of Galaxies — Their Structure, Motion, And Cosmic Evolution
According To Current Estimates, Dark Matter May Constitute Nearly 27% Of The Universe
Highlighting Its Significant Role In The Grand Cosmic Picture.
What Is Dark Energy? – Why Is The Universe Expanding So Rapidly?
When Scientists Observed Distant Supernovae (Exploding Stars Billions Of Light-Years Away),
They Discovered Something Astonishing —
The Universe Is Not Just Expanding…
Its Rate Of Expansion Is Accelerating!
Why Is The Universe Expanding So Fast?
Experts Suggest That This Accelerated Expansion Could Be Caused By An Invisible, Unknown Force
Which They Call Dark Energy.
What Does Dark Energy Actually Do?
While Gravity Pulls Matter Together,
Dark Energy Seems To Do The Opposite — It Drives Everything Apart.
This Is Why Scientists Believe Dark Energy Acts As A Repulsive Force,
Pushing Galaxies Away From Each Other, Causing The Universe To Expand Faster And Faster.
But What Exactly Is Dark Energy?
Just Like Dark Matter, Dark Energy Remains One Of The Biggest Cosmic Mysteries. So Far:
It Has Never Been Directly Observed
Its Existence Is Inferred From Indirect Evidence,
Like Supernova Data And Cosmic Expansion Measurements
Scientists Still Disagree On What It Actually Is Or How It Operates
In Simple Terms:
Dark Energy Is A Mysterious And Invisible Force
That Appears To Be Accelerating The Expansion Of The Universe.
But Its True Nature Remains Unknown —
And Scientists Around The World Are Still Conducting Intensive Research
To Unlock The Secrets Of This Puzzling Phenomenon.
The Fate Of The Universe – What Will Happen When Everything Ends?
If The Universe Continues To Expand At Its Accelerating Pace,
Then Scientists Propose A Fourth And Startling Scenario For The Distant Future:
Galaxies Will Vanish Forever
The Galaxies We Observe Today Will Gradually Recede Beyond Our Observable Horizon
Moving So Far Away That Their Light Will Never Reach Us Again.
One By One, They Will Disappear From View, Becoming Cosmically Unreachable.
Only The Milky Way Will Remain
After Billions Of Years, The Milky Way May Be The Only Galaxy Still Visible In Our Telescopes
All Others Will Have Faded Into Eternal Isolation, Lost In The Vastness Of Space.
The Sun Will Become A Cold White Dwarf
Our Sun Will Eventually Exhaust Its Nuclear Fuel,
Shrinking Into A White Dwarf — A Dim, Dying Star
Emitting Only A Faint Glow Of Heat And Light.
Stars Will Collapse Into Black Holes
All Stars Will Complete Their Stellar Lifecycles,
Slowly Burn Out, And Many Will Collapse Into Black Holes,
Leaving Behind Only Their Gravitational Remnants.
A Cold, Dark, And Lifeless Cosmos
Ultimately, The Universe Will Become A Place Of Absolute Stillness
A Realm That Is Cold, Dark, And Empty,
Where Energy Is Evenly Spread, And No New Structures Can Form.
Is This The Ultimate End?
According To This Theory, The Final Fate Of The Universe May Be One Of Permanent Darkness And Silence —
An Eternal State Where Nothing New Can Emerge, And All Activity Ceases Forever.
